Yantrik
Eligibility Criteria
| Trade | Age | Educational Qualification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yantriks (Technical Branch) | 18-22 years (5 Years relaxation for SC/ST, if the posts are reserved for them and 3 Years for OBC, if the posts are reserved for them) |
Class 10th passed from an education board recognized by Council of Boards for School Education (COBSE) and Diploma in Electrical/ Mechanical / Electronics/ Telecommunication (Radio/Power) Engineering of duration 03 or 04 years approved by All India Council of Technical Education (AICTE). OR Class 10th & Class 12th passed from an education board recognized by Council of Boards for School Education (COBSE) “AND” Diploma in Electrical/ Mechanical / Electronics/ Telecommunication (Radio/Power) Engineering of duration 02 or 03 years approved by All India Council of Technical Education (AICTE). Note : - List of equivalent diploma for recruitment in Yantrik cadre in Electrical, Mechanical and Electronics & Telecommunication (Radio/Power) Engineering (Engg) branch as mentioned below:-
|
Note:
- EWS candidates will not get any age relaxation.
- The Board for Class 10th and 12th must be recognised by Council of Boards of School Education in India (COBSE).
- Diploma must be recognised by All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE).
- Even if there is no vacancy reserved for SC / ST / OBC (Non - Creamy) / EWS category candidates, such candidates can still apply. However, they will not be eligible for any age and passing marks concession / relaxation etc. SC / ST candidates are exempt from payment of application fee even in such case.
Medical Standards
Medical examination will be conducted by authorized Military Doctors as per medical standard prescribed under current regulations applicable to the EP of Indian Coast Guard on entry. The detailed guidelines for medical standards are laid down in CG Order 26/2002 and 04/2013. Physical traits include minimum height of 157 cm with proportionate body weight, depending on the age and height of the candidate. He should also have proportionate chest with minimum expansion capability of 05 cms. Candidate should possess good mental and physical health, should be free from any disease/ disability and have no cardio-vascular disease, surgical deformities like Knock-Knees, Flat-Foot. Candidate should not have a past history of fits or psychiatric ailments, Varicose-veins etc. He should not have any type of infection in the ears. Candidates are advised to get their ears cleaned for wax and tartar removed from teeth before appearing for the written test, which is followed by PFT and Medical examination. Candidate should possess Colour perception standard of CP II and Eyes Visual standards should meet the under mentioned prescribed standards for both the conditions that is with glasses and without glasses.
Visual Standards
| Type of Entry | Without Glasses | With Glasses | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yantrik | Better eye | Worse eye | Better eye | Worse eye |
| 6/24 | 6/24 | 6/9 | 6/12 | |
Relaxation in Height
Minimum height permitted to a candidate for enrollment in the Indian Coast Guard is 157 cms. Tribal Candidates who pass written exam and PFT are to be granted relaxation in height as follows:-
| Domicile of Candidate | Min height standard after relaxation for induction/ recruitment into Indian Coast Guard as EP (in cms) |
|---|---|
| Assam, Nagaland, Mizoram, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Tripura, Garhwal, Sikkim, local tribes of Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
152 |
| Lakshadweep | 155 |
The candidates claiming height relaxation are to submit domicile certificate to the medical Officer. Failure to submit the domicile certificate will lead to non-waiver of height relaxation.
Weight
Proportionate to height and age +10 percentage acceptable.
Hearing
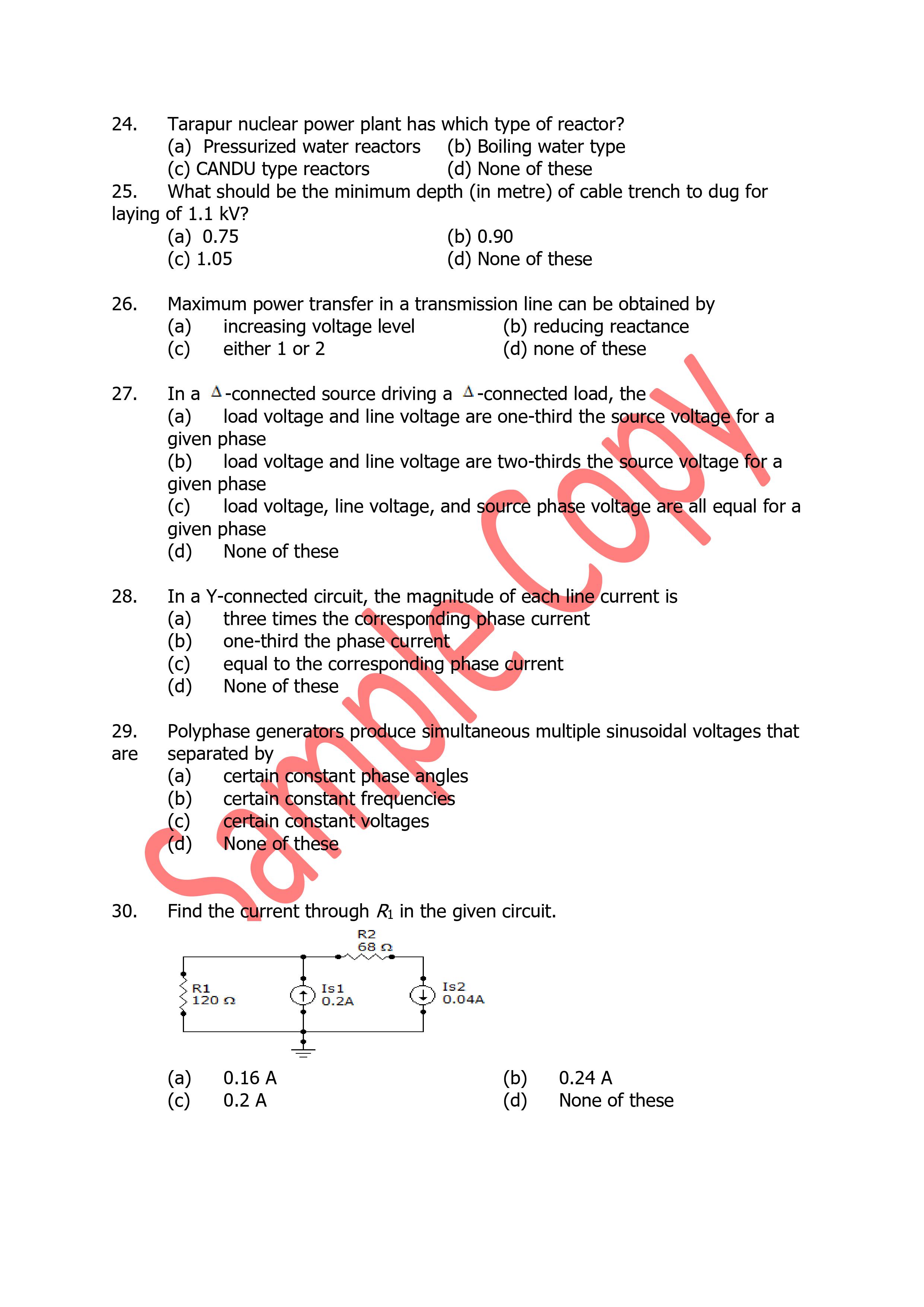
Normal
Tattoo
Permanent body tattoos are not permitted on any part of the body. However, certain concessions are permitted to candidates belonging to tribal areas communities as declared by the Govt. of India. For other candidates, permanent body tattoos are only permitted on inner face of forearms i.e. from inside of elbow to the wrist and on reverse side of palm/back (dorsal) side of hand. Please click here for tattoo policy regarding recruitment.
Note:
Candidates with above medical standards are only to appear for selection. No waiver will be given for above mentioned standards. The Indian Coast Guard (ICG) order on medical standard will be the final authority.
Section I
| Sr No. | Science | Mathematics | English | General Awareness | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Nature of Matter, Universe (Planets / Earth/Satellites/Sun), Electricity and its application | Mathematical Simplification, Ratio and Proportion, Algebric Identities, Linear Equations and Polynomials, Simultaneous Equations, Basic Trigonometry | Passage, Preposition, Correction of sentences, Change active to passive/passive to active voice. | Geography: Soil, Rivers, Mountains, Ports, Inland, Harbours | Spatial, Numerical Reasoning & Associative Ability, Sequences, Spellings Unscrambling, Coding and Decoding |
| 02 | Force and Gravitation, Newton’s Laws Of Motion, Work, Energy and Power | Simple Mensuration, Geometry, Measures of Central Tendency (Average, Median and Mode) | Change direct to indirect/indirect to direct, Verbs/Tense/Non Finites, Punctuation. | Culture and Religion, Freedom Movement, Important National Facts about India, Heritage, Arts and Dance | |
| 03 | Heat, Temperature, Metals and Non-Metals, Carbon and its Compounds, Measurements in Science, Sound & Wave Motion, Atomic Structure | Interest, Profit, Loss and Percentage, Work, Time, Speed and Distance | Substituting phrasal verbs for expression, Synonyms and Antonyms, Meanings of difficult words. | History, Defence, Wars and neighbours, Awards and Authors, Discoveries, Diseases and Nutrition | |
| 04 | - | - | Use of adjectives, Compound preposition. | Current Affairs, Languages, Capitals and Currencies, Common Names, Full Forms and Abbreviations | |
| 05 | - | - | Use of pronouns | Eminent Personalities, National
Bird/Animal/Sport /Flower/Anthem/ Song/ Flag/Mountains |
|
| 06 | - | - | - | Sports: Championships / Winners /Terms / Number of Players |
Note:- The syllabus of Science and Mathematics will be upto grade 10 of CBSE syllabus.
Section III
| Sr. No. | SUBJECT: Electrical Diploma Engineering | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Basic concepts- Concepts of resistance, inductance, capacitance, and various factors affecting them. Concepts of current, voltage, power, energy and their units. | |
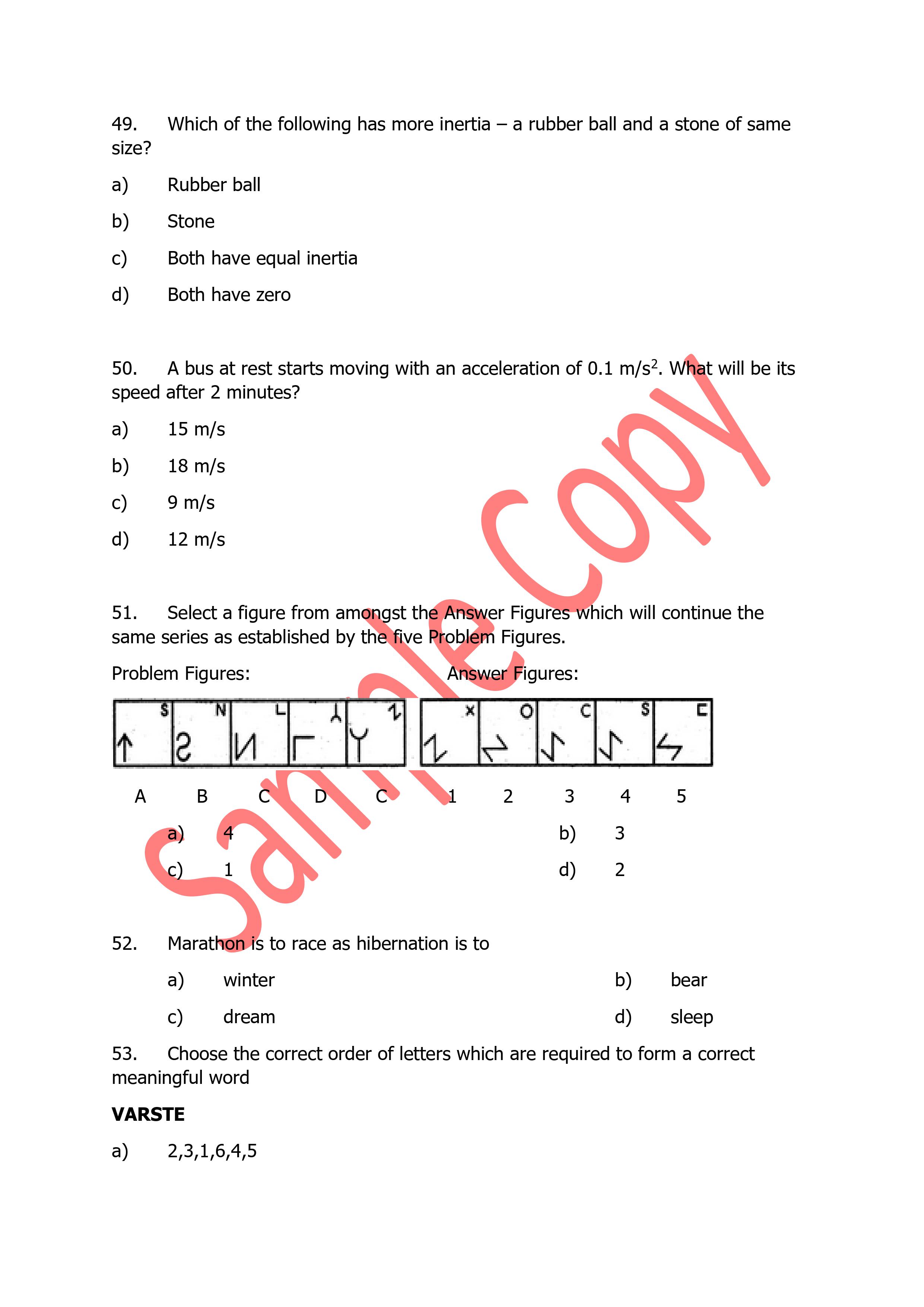
| 2 | Circuit law- Kirchhoff‘s law, Simple Circuit solution using network theorems. | |
| 3 | Magnetic Circuit- Concepts of flux, EMF, reluctance, Different kinds of magnetic materials, Magnetic calculations for conductors of different configuration e.g. straight, circular, solenoidal, etc. Electromagnetic induction, self and mutual induction. | |
| 4 | AC Fundamentals- Instantaneous, peak, R.M.S. and average values of alternating waves, Representation of sinusoidal wave form, simple series and parallel AC Circuits consisting of R.L. and C, Resonance, Tank Circuit. Poly Phase system – star and delta connection, 3 phase power, DC and sinusoidal response of R-Land R-C circuit. | |
| 5 | Measurement and measuring instruments- Measurement of power (1 phase and 3 phase, both active and re-active) and energy, 2 wattmeter method of 3 phase power measurement. Measurement of frequency and phase angle. Ammeter and voltmeter (both moving oil and moving iron type), extension of range wattmeter, Multimeters, Megger, Energy meter AC Bridges. Use of CRO, Signal Generator, CT, PT and their uses. Earth Fault detection. | |
| 6 | Electrical
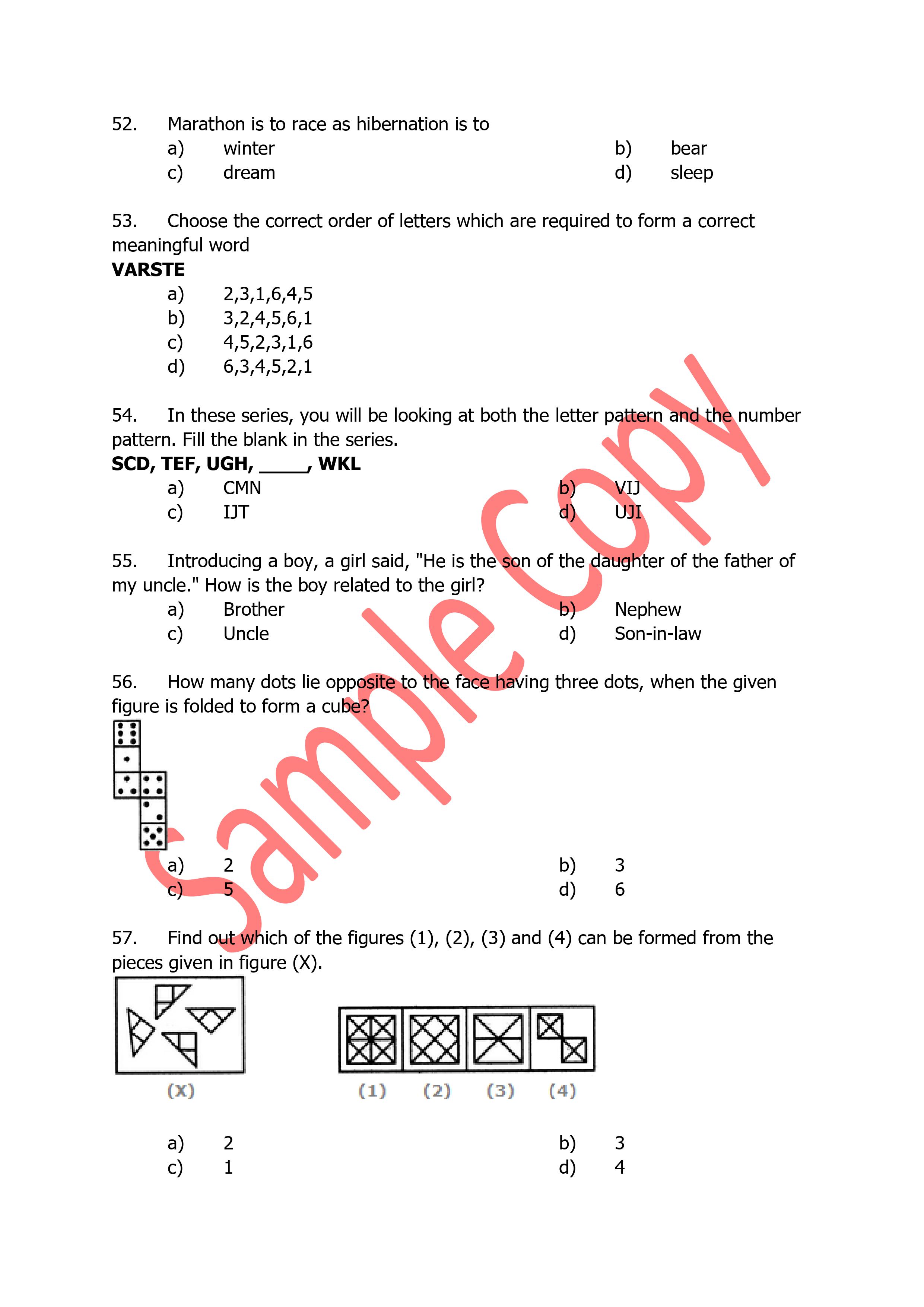
Machines- (a) D.C. Machine – Construction, Basic
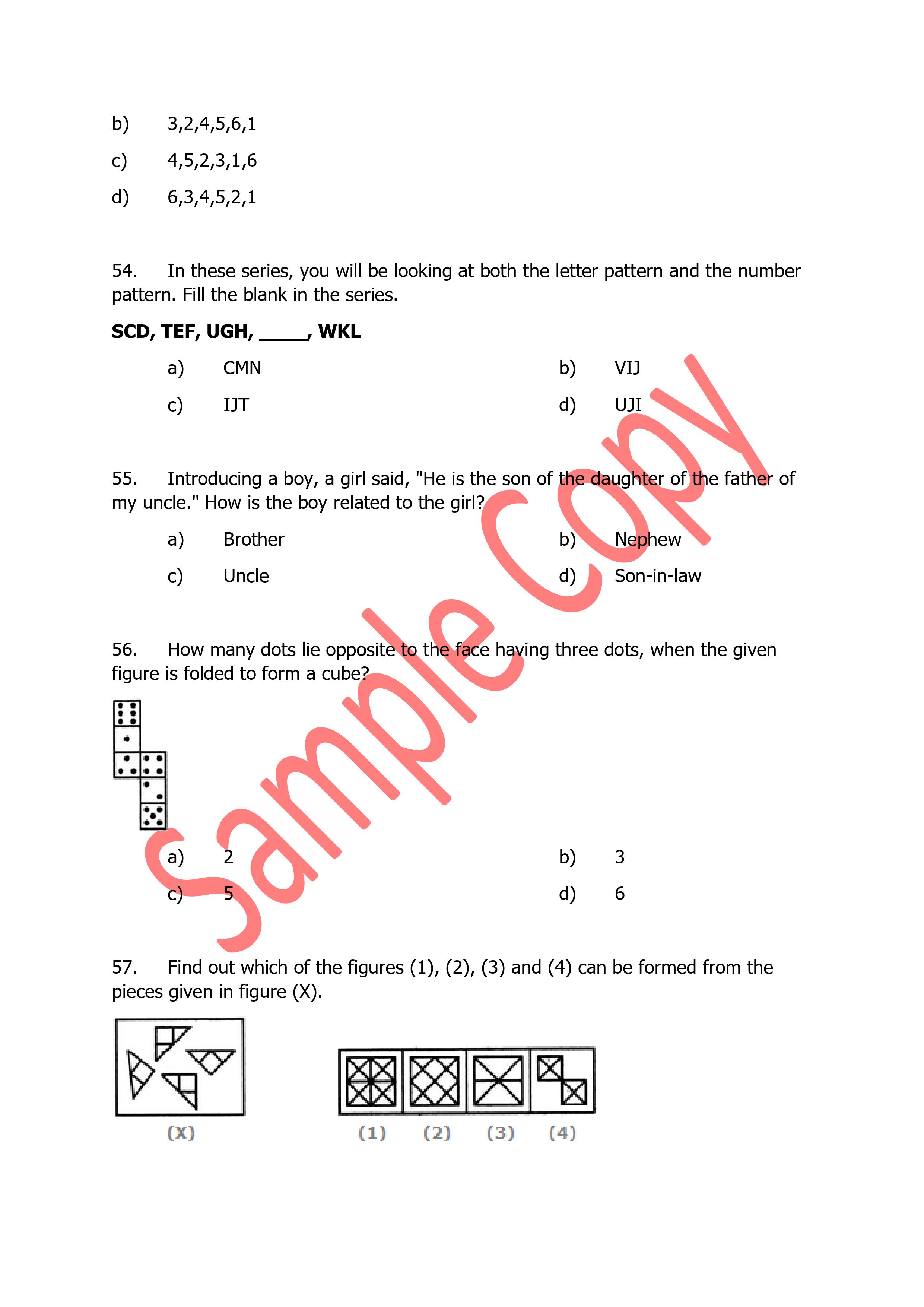
Principles of D.C. motors generators and their
characteristics, speed control and starting of D.C.
Motors. Method of braking motor, Losses and efficiency of
D.C. Machines. (b) 1 phase and 3 phase transformers – Construction, Principles of operation, equivalent circuit, voltage regulation, O.C. and S.C. Tests, Losses and efficiency. Effect of voltage, frequency and wave form on losses. Parallel operation of 1 phase /3 phase transformers. Auto transformers. (c) 3 phase induction motors, rotating magnetic field, principle of operation, equivalent circuit, torque-speed characteristics, starting and speed control of 3 phase induction motors. Methods of braking, effect of voltage and frequency variation on torque speed characteristics, Fractional Kilowatt Motors and Single Phase Induction Motors: Characteristics and applications. |
|
| 7 | Synchronous Machines- Generation of 3-phase e.m.f. armature reaction, voltage regulation, parallel operation of two alternators, synchronizing, control of active and reactive power. Starting and applications of synchronous motors. | |
| 8 | Generation,
Transmission and Distribution- Different types of power
stations, Load factor, diversity factor, demand factor,
cost of generation, inter-connection of power stations.
Power factor improvement, various types of tariffs, types
of faults, short circuit current for symmetrical faults. Switchgears and Protection-Rating of circuit breakers, Principles of arc extinction by oil and air, H.R.C. Fuses, Protection against earth leakage / over current, etc. Buchholz relay, Merz-Price system of protection of generators & transformers, protection of feeders and bus bars. Lightning arresters, various transmission and distribution system, comparison of conductor materials, efficiency of different system. Cable – Different type of cables, cable rating and derating factor. |
|
| 9 | Estimation And Costing- Estimation of lighting scheme, electric installation of machines and relevant IE rules. Earthing practices and IE Rules. | |
| 10 | Utilization of Electrical Energy- Illumination, Electric heating, Electric welding, Electroplating, Electric drives and motors. | |
| 11 | Basic Electronics- Working of various electronic devices e.g. PN Junction diodes, Transistors (NPN and PNP type), BJT and JFET. Simple circuits using these devices. | |
Section IV
| Sr. No. | SUBJECT: Electronics Diploma Engineering | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Basic concepts- Concepts of resistance, inductance, capacitance, and various factors affecting them. Concepts of current, voltage, power, energy and their units. | |
| 2 | Electronic Components & Materials- Conductors, Semi conductor& Insulators; Magnetic materials; Jointing & Cleaning materials for U/G copper cable & OFC; Cells and Batteries (chargeable and non chargeable); Relays, Switches, MCB & Connectors. | |
| 3 | Electronic Devices and Circuits- PN Junction diodes, thyristor; Diode and triode circuits; Junction Transistors; Amplifiers; Oscillator; Multivibrator, counters; Rectifiers; Inverter and UPS. | |
| 4 | Digital Electronics- Number System & Binary codes; Boolean Algebra & Logic gates; Combinational & Sequential logic circuits; A/D & D/A converter, counters; Memories. | |
| 5 | Linear Integrated Circuit- Introduction to operational Amplifier; Linear applications; Non Linear applications; Voltage regulators; Timers; Phase lock loop. | |
| 6 | Microprocessor and Microcontroller- Introduction to microprocessor, 8085 microprocessor working; Assembly Language programming; Peripherals & other microprocessors; Microcontrollers. | |
| 7 | Electronic Measurements- Measuring systems; Basic principles of measurement; Range Extension methods; Cathode ray oscilloscope, LCD, LED panel; Transducers. | |
| 8 | Communication Engineering- Introduction to communication; Modulation techniques; Multiplexing Techniques; Wave Propagation, Transmission line characteristics, OFC; Fundamentals of Public Address systems, Electronic exchange, Radar, Cellular and Satellite Communication. | |
| 9 | Data communication and Network- Introduction to data communication; Hardware and interface; Introduction to Networks and Networking devices; Local Area Network and Wide area network; Internet working. | |
| 10 | Computer Programming- Programming concepts; Fundamentals of ‘C’ and C ++; Operators in ‘C’ and C ++; Control Statements; Functions, Array String & Pointers, File Structure; Data Structure and DBMS. | |
| 11 | Basic Electrical Engineering- DC Circuits; AC fundamentals; Magnetic, Thermal and Chemical effects of Electric current; Earthing - Installation, Maintenance, Testing. | |
Section V
| Sr. No. | SUBJECT: Mechanical Engineering Diploma | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Engineering Mechanics- Resolution of forces, Equilibrium and Equilibrant, parallelogram law of forces, triangle law of forces, polygon law of forces and Lami’s theorem, couple and moment of a couple, condition for equilibrium of rigid body subjected to number of coplanar non-concurrent forces, definition of static friction, dynamic friction, derivation of limiting angle of friction and angle of repose, resolution of forces considering friction when a body moves on horizontal plane and inclined plane, calculation of moment of inertia and radius of gyration of : (a) I-Section (b) channel section (c) T-Section (d) L-Section (Equal & unequal lengths) (e) Z-Section (f) Built up sections (simple cases only), Newton’s laws of motion (without derivation), motion of projectile, D’Alembert’s principle, definition law of conservation of energy, law of conservation of momentum. | |
| 2 | Material Science- Mechanical properties of engineering materials – tensile strength, compressive strength, ductility, malleability, hardness, toughness, brittleness, impact strength, fatigue, creep resistance. Classification of steels, mild steel and alloy steels. Importance of heat treatment. Heat treatment processes – annealing, normalizing, hardening, tempering, carburizing, nitriding and cyaniding | |
| 3 | Strength of Materials- Stress, strain, stress strain diagram, factor of safety, thermal stresses, strain energy, proof resilience and modules of resilience. Shear force and bending moment diagram – cant leaver beam, simply supported beam, continuous beam, fixed beam. Torsion in shafts and springs, thin cylinder shells. | |
| 4 | Machining- Working principle of lathe. Types of lathes – Engine lathe – construction details and specifications. Nomenclature of single point cutting tool, geometry, tool signature, functions of tool angles. General and special operations – (Turning, facing, taper turning thread cutting, knurling, forming, drilling, boring, reaming, key way cutting), cutting fluids, coolants and lubricants. Introduction to shaper, slotter, plainer, broaching, milling and manufacture of gears, heat treatment process applied to gears. | |
| 5 | Welding- Welding – Introduction, classification of welding processes, advantages and limitations of welding, principles of arc welding, arc welding equipment, choice of electrodes for different metals, principle of gas (oxy-acetylene) welding, equipment of gas welding, welding procedures (arc & gas), soldering and brazing techniques, types and applications of solders and fluxes, various flame cutting processes, advantages and limitations of flame cutting, defects in welding, testing and inspection modern welding methods, (submerged, CO2, atomic – hydrogen, ultrasonic welding), brief description of MIG & TIG welding. | |
| 6 | Grinding & Finishing Process- Principles of metal removal by grinding, abrasives, natural and artificial, bonds and binding processes, vitrified, silicate, shellac rubber, grinding machines, classification: cylindrical, surface, tool & cutter grinding machine, construction details, relative merits, principles of centreless grinding, advantages & limitations of centreless grinding work, holding devices, wheel maintenance, balancing of wheels, coolants used, finishing by grinding, honing, lapping, super finishing, electroplating, basic principles – plating metals, applications, hot dipping, galvanizing tin coating, parkerising, anodizing, metal spraying, wire process, powder process and applications, organic coatings, oil base paint, lacquer base enamels, bituminous paints, rubber base coating. | |
| 7 | Metrology- Linear measurement – Slip gauges and dial indicators, angle measurements, bevel protractor, sine bar, angle slip gauges, comparators (a) mechanical (b) electrical (c) optical (d) pneumatic. Measurement of surface roughness; methods of measurements by comparison, tracer instruments and by interferometry, collimators, measuring microscope, interferometer, inspection of machine parts using the concepts of shadow projection and profile projection. | |
| 8 | Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulic Machinery- Properties of fluid, density, specific weight, specific gravity, viscosity, surface tension, compressibility capillarity, Pascal’s law, measurement of pressures, concept of buoyancy. Concept of Reynold’s number, pressure, potential and kinetic energy of liquids, total energy, laws of conservation, mass, energy and momentum, velocity of liquids and discharge, Bernoulli’s equation and assumptions, venturimeters, pitottube, current meters. Working principle & constructional details of centrifugal pump, efficiencies – manometric efficiency, volumetric efficiency, mechanical efficiency and overall efficiency, cavitation and its effect, working principle of jet & submersible pumps with line diagrams. | |
| 9 | Industrial Management- Job analysis, motivation, different theories, satisfaction, performance reward systems, production, planning and control, relation with other departments, routing, scheduling, dispatching, PERT and CPM, simple problems. Materials in industry, inventory control model, ABC Analysis, Safety stock, re-order, level, economic ordering quantity, break even analysis, stores layout, stores equipment, stores records, purchasing procedures, purchase records, Bin card, Cardex, Material handling, Manual lifting, hoist, cranes, conveyors, trucks, fork trucks. | |
| 10 | Thermal Engineering- Laws of thermo dynamics, conversion of heat into work vice versa , laws of perfect gases, thermo dynamic processes – isochoric, isobaric, isothermal hyperbolic, isentropic, polytrophic and throttling, modes of heat transfer, thermal conductivity, convective heat transfer coefficient, Stefan Boltzman law by radiation and overall heat transfer coefficient. Air standards cycles – Carnot cycle, Otto cycle, Diesel cycle, construction and working of internal combustion engines, comparison of diesel engine and petrol engine. Systems of internal combustion engine, performance of internal combustion engines. Air compressors their cycles refrigeration cycles, principle of a refrigeration plant | |
Recruitment Cycle
ICG carries out bi-annual recruitment for Yantrik (Mechanical, Electrical and Electronics) as per the following tentative schedule.
| Sl | Post | Application Registration | Stage I Written Exam |
Stage II PFT/ Medical |
Stage III/ Induction in Indian Coast Guard |
Stage IV Original Document Verification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Batch Cycle | ||||||
| (a) | Yantrik (Mechanical) | Sep (Previous Year) | Mid Nov (Previous Year) | Jan (Next Year) | Apr/May (Next Year) | Apr/May (Next Year) |
| (b) | Yantrik (Electrical) | Sep (Previous Year) | Mid Nov (Previous Year) | Jan (Next Year) | Apr/May (Next Year) | Apr/May (Next Year) |
| (c) | Yantrik (Electronics / Telecommunication (Radio/ Power)) | Sep (Previous Year) | Mid Nov (Previous Year) | Jan (Next Year) | Apr/May (Next Year) | Apr/May (Next Year) |
| Second Batch Cycle | ||||||
| (d) | Yantrik (Mechanical) | Jan (Previous Year) | Mid Mar (Previous Year) | May (Previous Year) | Aug/Sep (Previous Year) | Aug/Sep (Next Year) |
| (e) | Yantrik (Electrical) | Jan (Previous Year) | Mid Mar (Previous Year) | May (Previous Year) | Aug/Sep (Previous Year) | Aug/Sep (Next Year) |
| (f) | Yantrik (Electronics / Telecommunication (Radio/ Power)) | Jan (Previous Year) | Mid Mar (Previous Year) | May (Previous Year) | Aug/Sep (Previous Year) | Aug/Sep (Next Year) |
Note:- The advertisement for the above recruitment cycle is generally published as follows:
- First Batch Cycle- Aug/Sep
- Second Batch Cycle- Dec/Jan
Selection Procedure
The selection of candidate is on order of merit list {all India for Yantrik} based on their performance in Stage-I, II, III & IV and the number of vacancies available for the post. Clearing of Stage-I, II, III, IV and satisfactory performance in training is compulsory for recruitment in ICG. All candidates will be compulsorily subjected to identity check prior commencement of the examination of Stage- I, II, III of CGEPT.
The identity check will include verification/matching of following at all four stages of selection procedure:-
- Live Image Capture during Registration – The candidate has also to upload the latest photograph during registration. Additionally, live image of the candidate will be captured during the registration. The facial features of the candidate in the uploaded photo will be matched against the Real-time photo. The candidate will be able to submit the application, only in case of photo match. Moreover, photograph of candidate in application form will be matched with facial features/Physical appearance of the candidate at subsequent Stages.
- Biometric –
- Only left thumb biometric will be captured at the Stage-I recruitment. In case the biometric of left thumb is not captured during Stage-I then the biometric of right thumb will be captured and will be used for subsequent verification. Apart from left and right thumb, no other finger will be considered for the biometric.
- It is candidate’s responsibility to check before hand that the biometric machines are able to capture the fingerprint image. In case, if the biometric machine is not able to capture the fingerprint image due to Mehndi, wax, etc. then, the candidate will not be allowed to appear in the examination.
- Signature as uploaded in online application.
- Identification mark as mentioned in online application.
Note: Failure in even one of the above mentioned identity check at any stage will lead to cancellation of candidature. The candidates to check various examples for filling of name, father’s name, identity card number and date of birth prior filling online application.
The details of various stages of CGEPT examination are as follows: -
Stage-I : (Computer Based Examination).
(a) Document verification (‘Provisionally Pass’ or ‘Fail’): At Stage-I candidate’s identity will be checked against the details filled by candidate in online application. The candidates will be required to bring following documents for verification while reporting at their respective examination centre:-
- Valid original Identity proof (Aadhaar Card OR PAN Card OR Voter ID card OR Driving License OR Passport) as submitted/uploaded in online application. The candidates possessing Aadhaar Card are to upload the Aadhaar Card as first option for identity proof while filing the online application.
- 01 Coloured printout of E-admit card (black & white print out not allowed).
- 02 in no. passport size colour photograph with similar facial features as uploaded in online application.
- For SC/ST applicants only: - Original category certificate and 02 photocopy of selfattested SC/ST certificate, original train/bus ticket, cancelled cheque leaf for NEFT payment and travel form downloaded from website for claiming TA.
Note: The details of candidate (Name, Identity proof details, DoB) mentioned in online application & E-admit card will be matched with Identity proof (Aadhaar Card OR PAN Card OR Voter ID card OR Driving License OR Passport) uploaded by candidate in online application. Any discrepancy in Name/DoB/Identity card no./Photograph in above documents with respect to information in online application & E-admit card will lead to cancellation of candidature. It is to be noted that no other document will be checked at Stage-I and it’s only a preliminary basic document verification. The detailed document verification will be carried out at Stage-II and Stage-III as per rules mentioned in succeeding paragraphs.
(b) Biometric Recording: Candidates who clears document verification will undergo biometric recording at Stage-I. The biometric data captured at Stage-I will be verified/recaptured at subsequent stages i.e. Stage-II, Stage-III & Stage-IV.
(C) The candidate has to take following tests depending on post applied:
| Sr. No. | Post Applied | Written Test | Passing Marks | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (i) | Yantrik (Electrical) | Section (I+III) | 30+20= 50 (UR/ EWS/ OBC) 27+17= 44 (SC/ST) | Passing in section I and III separately is compulsory |
| (ii) | Yantrik (Electronics) | Section (I+IV) | 30+20= 50 (UR/ EWS/ OBC) 27+17= 44 (SC/ST) | Passing in section I and IV separately is compulsory |
| (iii) | Yantrik (Mechanical) | Section (I+V) | 30+20= 50 (UR/ EWS/ OBC) 27+17= 44 (SC/ST) | Passing in section I and V separately is compulsory |
Note: Yantrik candidates can apply for only one post either for Electronics or Electrical or Mechanical.
(d) The details of various section are as follows:
| Sr. No. | Name Of Examination | Details of Examination | Subject wise allocation of Questions | Pass Marks | Syllabus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (i) | Section I | Maximum Marks – 60, Time – 45 mins., Total no. of Questions – 60 | Maths – 20, Science - 10, English – 15, Reasoning–10, GK – 5 | 30 (UR/EWS/OBC category), 27 (for SC/ST category) | Class 10th Syllabus |
| (ii) | Section III | Maximum Marks – 50, Time – 30 mins., Total no. of Questions – 50 | Electrical Engineering - 50 | 20 (UR/EWS/ OBC category), 17 (for SC/ST category) | Diploma Level Electrical Engineering syllabus |
| (iii) | Section IV | Maximum Marks – 50, Time – 30 mins., Total no. of Questions – 50 | Electronics Engineering - 50 | 20 (UR/EWS/ OBC category), 17 (for SC/ST category) | Diploma Level Electronics Engineering syllabus |
| (iv) | Section V | Maximum Marks – 50, Time – 30 mins., Total no. of Questions – 50 | Mechanical Engineering - 50 | 20 (UR/EWS/ OBC category), 17 (for SC/ST category) | Diploma Level Mechanical Engineering syllabus |
(e) Normalisation of Marks In order to rationalise the marks scored by candidates appearing in different shifts in an objective manner through a statistical method, before declaration of result, marks scored by candidates will be normalised as per the following formula:-

- Where:
Mij = Normalised maks of jth candidate in the ith shift. - Mtg = is the average marks of the top 0.1% of the candidates considering all shifts (number of candidates will be rounded-up)
- Mqg= is the sum of mean and standard deviation marks of the candidates in the examination considering all shifts.
- Mti = is the average marks of the top 0.1% of the candidates in the ith shift (number of candidates will be rounded-up)
- Miq = is the sum of mean marks and standard deviation of the ith shift.
- Mij = is the actual marks obtained by the jth candidate in the ith shift.
- Mqgm = is the sum of mean marks of candidates in the shift having maximum mean and standard deviation of marks of candidates in the examination considering all shifts.
Note:
(aa) The question paper for section I,
III, IV & V will be objective type with four options. The
candidate has to choose the correct option. There is no
negative marking in the written examination test. The detailed
syllabus for section I, III, IV & V is available on ICG
website.
(ab) Tie
Breaking Rule in Merit - In case of two or more candidates
having the same marks in stage I then the tie will be broken
in steps as follows (wherever tie is broken next stage will
not be proceeded):
(i) Candidate scoring more marks in section –I.
(ii)
Candidate scoring more aggregate percentage (upto three
decimal places) in Diploma will be considered by the
Recruiting Authority based on marks/ CGPA entered by the
applicant/ candidate and aggregate percentage will be
calculated on the basis of top five scoring subjects as
promulgated by the Board of Education/ University.
(iii) Candidate older in age will be higher in merit.
STAGE-II:
Based on performance in Computer Based Examination and
handling capacity of ICG Recruitment Centres candidates will
be shortlisted for Stage-II and provisional E-admit card is
issued. To download E-admit card, candidates are required to
upload additional documents as mentioned here.
Failure to upload additional documents within the time frame
promulgated by ICG will lead to cancellation of candidature.
The duration of Stage-II is 1-2 days and will be conducted at
allocated centre. Stage-II involves following examination
which are only qualifying in nature i.e. either provisionally
‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’:-
Assessment/Adaptability Test. Biometric verified candidates will undergo OMR based written examination. This test is just qualifying in nature and the marks obtained will not be included in final merit list. The result will be announced after an hour of conduct of examination. Those who qualify this test will only proceed for the next phase of examination i.e. PFT.
(a) Physical Fitness Test (Pass/Fail): Candidates undergoing PFT will do so at their own risk. All candidates are advised to be in possession of sports rig (Shoe, T-shirt, Trouser etc). The PFT consists of:-
- 1.6 Km run to be completed in 7 minutes.
- 20 Squat ups (Uthak Baithak).
- 10 Pushup.
All three test of PFT are to be carried out in continuity without any break. Any break in three tests will lead to failing the PFT.
(b) Document verification (Provisionally Pass/Fail)
All information provided in online application has to match
with all original documents produced by the candidate like
Class 10th /Class 12th /Diploma marksheet/Identity proof
(Aadhaar Card OR PAN Card OR Voter ID card OR
Driving License OR Passport)/ category
certificate/individual subject and aggregate marks/CGPA (as
applicable). Any mismatch/inconsistency/error with
information provided by the candidate in application form,
uploaded document and original documents produced for
verification at Stage-II with the documents in respect to
“Name, Date of birth, Parent’s name, subject wise marks/CGPA
(as applicable), validity of documents, category certificate
details etc.” will lead to failure in document verification
and the candidature will be cancelled. The date of
issue of all documents has to be on or before the closing
date of application. The validity of all uploaded documents
has to be at least up to 30 Apr 25. Any false
declaration in the online application will lead to
cancellation of candidature. Common reasons for rejection can
be checked at Reasons
For Rejection
(c) Recruitment Medical Examination.
The Medical Officer will assess the candidates for medical
fitness as per laid down medical standards and declare them
fit/unfit. Candidates declared unfit and who wish to appeal
will be referred to any designated appeal medical centre
(allocated by ICG). Such candidates are to report to
the appeal medical centre within a maximum period of 21 days
from the date of recruitment medical examination which has
declared them unfit. No other Medical fitness certificate
other than that of the specialist opinion in a military
hospital is admissible during appeal medical.The appeal
medical examination will be considered as final and the
candidate will have no right for further appeal at any other
or same hospital again.
Note :
- The schedule in conduct of recruitment medicals may change and may be conjoined with pre-enrolment medicals at any stage as per discretion of recruiting authority, subject to administrative or technical reasons.
- Candidates declared fit in recruitment medical examination at Stage-II recruitment centre, may be disqualified in document verification during the further scrutiny of the documents by ICG as the document verification is carried out at multiple stages of recruitment procedure even after the conduct of Stage-II prior publishing the final merit/ result as mentioned in para 13(ak) below.
- Non-completion of the medicals (Initial recruitment & appeal) prior four (04) weeks of induction date to the training academy (INS Chilka) may lead to the cancellation of candidature.
(d) Preparation of Final Merit List for Stage-III
ICG will carry out the re-verification (in the absence of
candidates) of documents submitted by candidates and only
those candidates will be considered for merit preparation who
will qualify the document verification and declared fit in
initial/appeal medicals. Merit list (Region/Zone wise for
Nvk(GD) and all India for Yantriks) will be prepared based on
marks scored by candidate in Stage-I and number of available
vacancies. The tie-Breaking Rule in Merit, in case of two or
more candidates having the same marks in Stage -I, is as
follows (wherever tie is broken next stage will not be
preceded):-
- Candidate scoring more marks in Section–I.
- Candidate older in age will be higher in merit.
STAGE-III
The candidates who qualify Stage-I & Stage-II and stands in merit as per the vacancies available will be provisionally shortlisted for training at INS Chilka and will be issued with provisional E-admit card. The duration of Stage-III is 1-2 days. Further, as INS Chilka is a Naval training establishment, verification procedure at training base in vogue are applicable. Stage-III involves following:-
(a) Document Verification (Provisionally ‘Pass’ or
‘Fail’).
All information provided in online application has to match
with all original documents produced by the candidate like
Class 10th /Class 12th /Diploma marksheet/Identity proof
(Aadhaar Card OR PAN Card OR Voter ID card OR Driving License
OR Passport)/Domicile Certificate/category
certificate/individual subject and aggregate marks/CGPA (as
applicable). Any mismatch/inconsistency/error with
information provided by the candidate in application form,
uploaded document and original documents produced for
verification at Stage-II with the documents in respect to
“Name, Date of birth, Parent’s name, subject wise marks/CGPA
(as applicable), validity of documents, category certificate
details etc.” will lead to failure in document verification
and the candidature will be cancelled. The date of issue of
all documents has to be on or before the closing date of
application. The validity of all uploaded documents has to be
at least up to 30 Apr 25. Any false declaration in the online
application will lead to cancellation of candidature. Common
reasons for rejection can be checked at
Reasons For Rejection
(b) Final Recruitment Medicals at INS Chilka.
The final recruitment medical examination of all selected
candidates will be done at INS Chilka. The conduct of final
recruitment medical examination will depend on the time gap
between recruitment medical examination conducted during
Stage-II recruitment process and date of reporting of
candidates at INS Chilka. Candidates declared Unfit during
final recruitment medical will be given a chance for appeal,
if they so desire at the designated appeal medical centre
(INHS Nivarini/INHS Kalyani) within a maximum period of 21
days of being declared unfit. The candidate will travel to
the selected Military Hospital and back on their own expense
for Appeal Medical Examination.
Note : The
schedule for conduct of final recruitment medicals may change
as per discretion of recruiting authority, subject to
administrative or technical reasons.
(c) Submission of original document, police
verification and other associated forms
All candidates are to submit original documents, police
verification forms and other associated forms along with the
E-admit card at Stage-III. Candidates should be in possession
of police verification from either place of domicile or place
of present residence which should have been obtained after
last date of submission of application form. Candidates
without verified police verification reports or reports with
adverse comments will not be eligible for enrolment. The
format for the police verification form can also be
downloaded from here.
STAGE–IV:
The candidates undergoing training at INS Chilka are to submit
all original documents during Stage-III and verification of
all original documents through Boards/Universities/State
government will be carried out by Indian Coast Guard.
Candidate will be terminated from service if documents are
reported as not genuine by respective
Boards/Universities/State government.
Training
The basic training for Yantrik (Mechanical, Electrical,
Electronics) will be conducted at INS Chilka followed by sea
training and professional training in the allotted trade.
Branch/ trade will be allocated as per the requirement of
service and performance during basic training. Basic training
at INS Chilka will cover the following Subjects:
(b) Sports activities
(c) Outdoor training such as Parade Training, Sailing, Boat Pulling, Swimming, Trekking, Cross- Country, Firing etc.
(d) Service oriented activities including maintenance of equipment, living spaces and training areas etc.
Duration of Training
Yantrik (Mechanical, Electrical, Electronics) – 16 weeks
Note:
- On completion of basic training at INS Chilka, the trainee will undergo professional and sea training for a period of 06 months to 2 years or as decided by ICG.
- Yantrik (Mechanical, Electrical, Electronics) are liable to be discharged as UNSUITABLE if their progress (including academic) or conduct is unsatisfactory at any time during training. Trainees are also liable to be discharged at any stage of training if their online application or the documents are found to be falsified at the stage of recruitment.
Benefits
- Free ration and clothing as per the existing rules. Free medical treatment for self and family including dependent parents.
- Government accommodation for self & family on nominal license fee.
- 45 days Earned leave and 08 days Casual leave every year with Leave Travel Concession (LTC) for self, family and dependent parents as per Government rules.
- Contributory Pension Scheme and Gratuity on retirement.
- Canteen and various loan facilities.
- ECHS medical facilities after retirement.
- Insurance cover (on contribution) of Rs. 50 lakhs for Enrolled Personnel is applicable.
Note: Benefits are subject to change as per government directives issued from time to time.
Pay and Allowances
| Rank | Pay |
|---|---|
| Yantrik | Basic pay Rs. 29200/- (Pay Level-5). In addition, you will be paid Yantrik pay @ Rs. 6200/- plus Dearness Allowance and other allowances based on nature of duty/place of posting as per the prevailing regulation |
Note: Pay and Allowances are subject to change as per government directives issued from time to time.
Career Progression
Enrolled personnel joining ICG as Yantrik (Mechanical, Electrical and Electronics) get optimum career progression opportunity for further promotion to the higher ranks. The rank structures and required minimum time period for promotion to next higher rank for Yantrik (Mechanical, Electrical and Electronics) is as follows:
Rank Structure
Pradhan Sahayak Engineer
Uttam Sahayak Engineer
Sahayak Engineer
Pradhan Yantrik
Uttam Yantrik
Yantrik
Yantrik (Mechanical, Electrical and Electronics)
| Cadre | Rank | Minimum time period in one rank for promotion |
|---|---|---|
| YANTRIK | YANTRIK - UTTAM YANTRIK | 2 Yrs |
| YANTRIK | UTTAM YANTRIK – PRADHAN YANTRIK | 2 Yrs |
| YANTRIK | PRADHAN YANTRIK - SAHAYAK ENGINEER | 3 Yrs |
| YANTRIK | SAHAYAK ENGINEER - UTTAM SAHAYAK ENGINEER | 4 Yrs |
| YANTRIK | UTTAM SAHAYAK ENGINEER – PRADHAN SAHAYAK ENGINEER | 3 Yrs |
Promotion to Officer’s Cadre : The Enrolled Personnel may also get opportunity for promotion to the Officer’s Rank if fulfilling the requisite criteria promulgated by Indian Coast Guard from time to time.
Note: Promotion rules are subject to change as per government regulations in vogue.
Job Profile
Yantrik serves on-board ships and aircraft as per the branch allocated to them {Mechanical, Electrical, Electronics / Telecommunication (Radio/Power)} at INS Chilka. They are responsible to maintain all types of the machinery/ equipment fitted on-board Ships/ Aircraft/ Station. They are also required to maintain the adequate level of spares and accounting of the spares.